
AU tasks: Comparison of sediment eDNA with traditional species abundance data during soft-sediment MSFD monitoring in the Danish North Sea.
It is a challenge that traditional zoo-benthos haps core-sampling in the soft-bottom sediment of the Danish North Sea typically covers in the order of about 10-10 of the habitat of interest. Thus rare species are seldom included or they are poorly quantified. Within this case study, eDNA-based methods will be will be compared with the traditional zoo-benthos haps core-sampling of soft sediment by sampling intact sediment cores of ca 7 cm with a diameter of ca 2 cm were sampled on deck from the haps core-sampler. The samples were immediately stored at -20°C.

Using eDNA metabarcoding with universal eukaryote primers Molecular – Operational Taxonomic Units (M-OTUs) will be determined. Using bioinformatics analyses, these data enable us to:
More than 200 sediment samples were collected from Danish stations during April 23-25 2019.
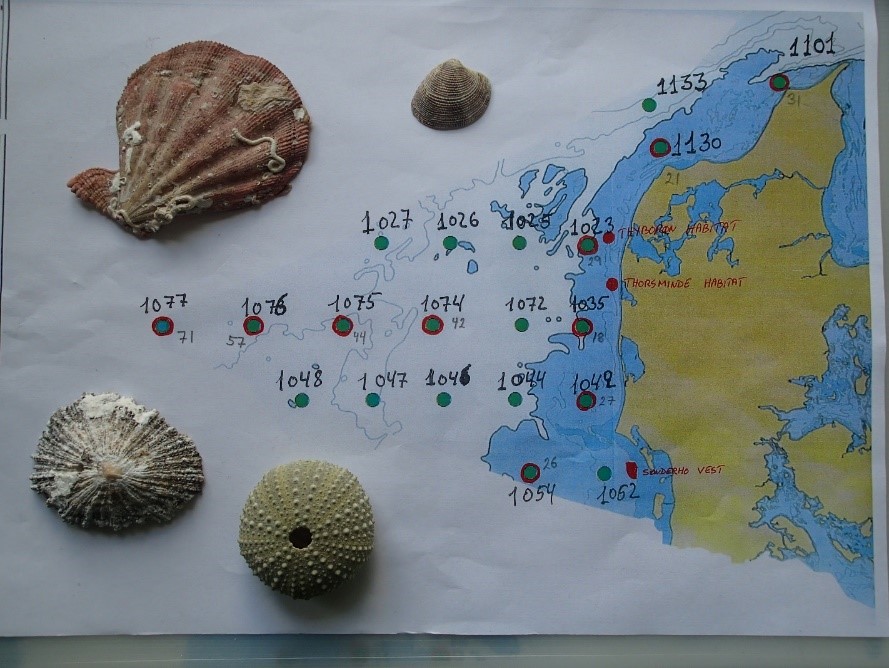
Photo showing stations sampled (red circle) in the Danish North Sea Region
3. DNAquaNet COST Action CA15219 https://dnaqua.net/
4. Strategic Growth Area environmental DNA (http://envs.au.dk/forskning/strategic-growth- areas/sga-dna/ )